Product Solution 2
Established Practice:
The dominant CO2 sensing technology is based on optical technology, more specifically NDIR, whereby the light absorbed to promote excitation in the CO2 molecule provides the means of detection. Although offering precise measurement, it is component-rich (a light source, a light detector, an optical tube/path, mirrors, reflectors, optical filters and ancillary circuitry), making it costly, fragile and totally unsuitable to hot and humid environments. Advances in reducing the size have been made but the inherent dependence of accuracy on size restricts shrinkage to centimetre scale.
McGowan solution:
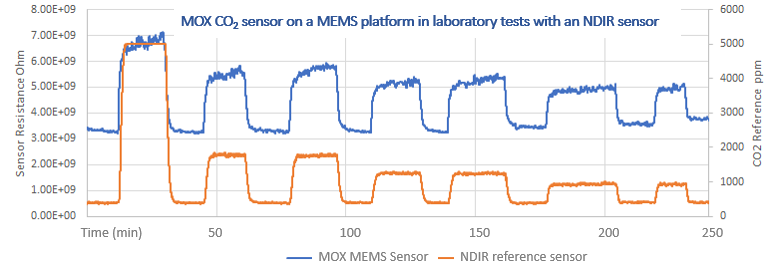
We developed a MOX CO2 sensor, which won a prestigious UK SMART award. Unlike the traditional MOX materials, our novel material responds to CO2 gas but not to VOCs - offering the possibility of CO2 measurement indoors, outdoors, in automotive, for personal use, at a significantly lower cost-point.
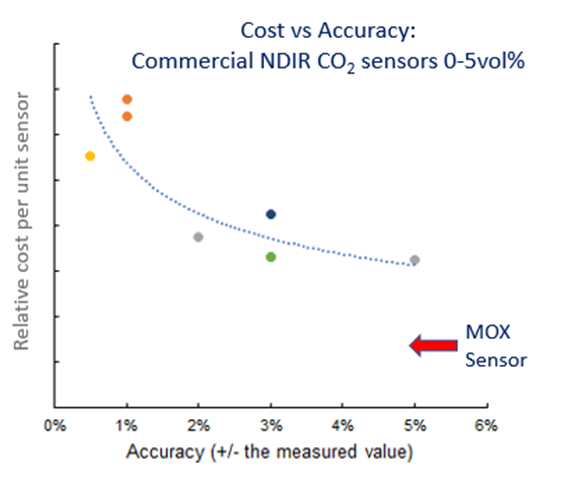
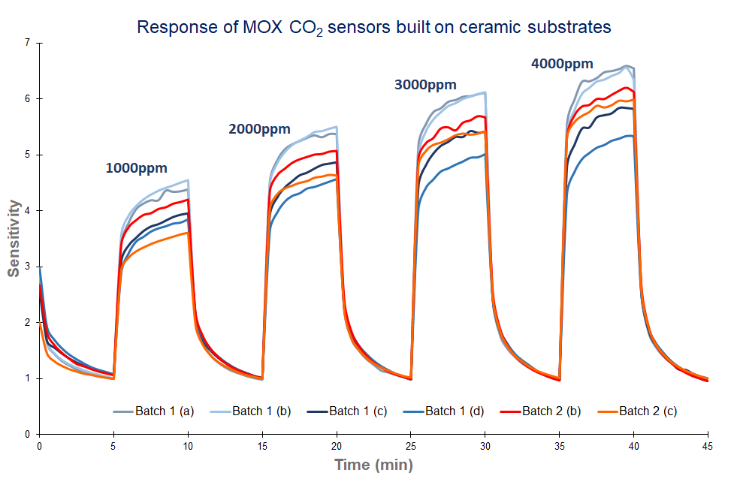
This technology is potentially disruptive, as it can enter the market at a significantly lower
price, albeit at the lower quality end but 'good enough' for most applications. With time,
advances will lead to higher accuracy levels.